2025-09-30 テキサス大学オースチン校(UT Austin)
<関連情報>
- https://news.utexas.edu/2025/09/30/study-finds-dietary-changes-quickly-alter-brain-markers-linked-to-memory-and-inflammation/
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11011-025-01624-8
低炭水化物・低カロリー食は、代謝機能障害関連脂肪肝疾患(MASLD)患者の肝臓脂肪を減らし、脳内グルタミン酸およびミオイノシトール濃度を低下させる Low carbohydrate and low-calorie diets reduce liver fat and lower brain glutamate and myo-inositol levels in patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
Andreana P. Haley,Jack Knight-Scott,Marie Caillaud,Isabelle Gallagher,Jessica Park,Yanrong Li,Tianyu Wang,Hirofumi Tanaka & Jeffrey D. Browning
Metabolic Brain Disease Published:10 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-025-01624-8
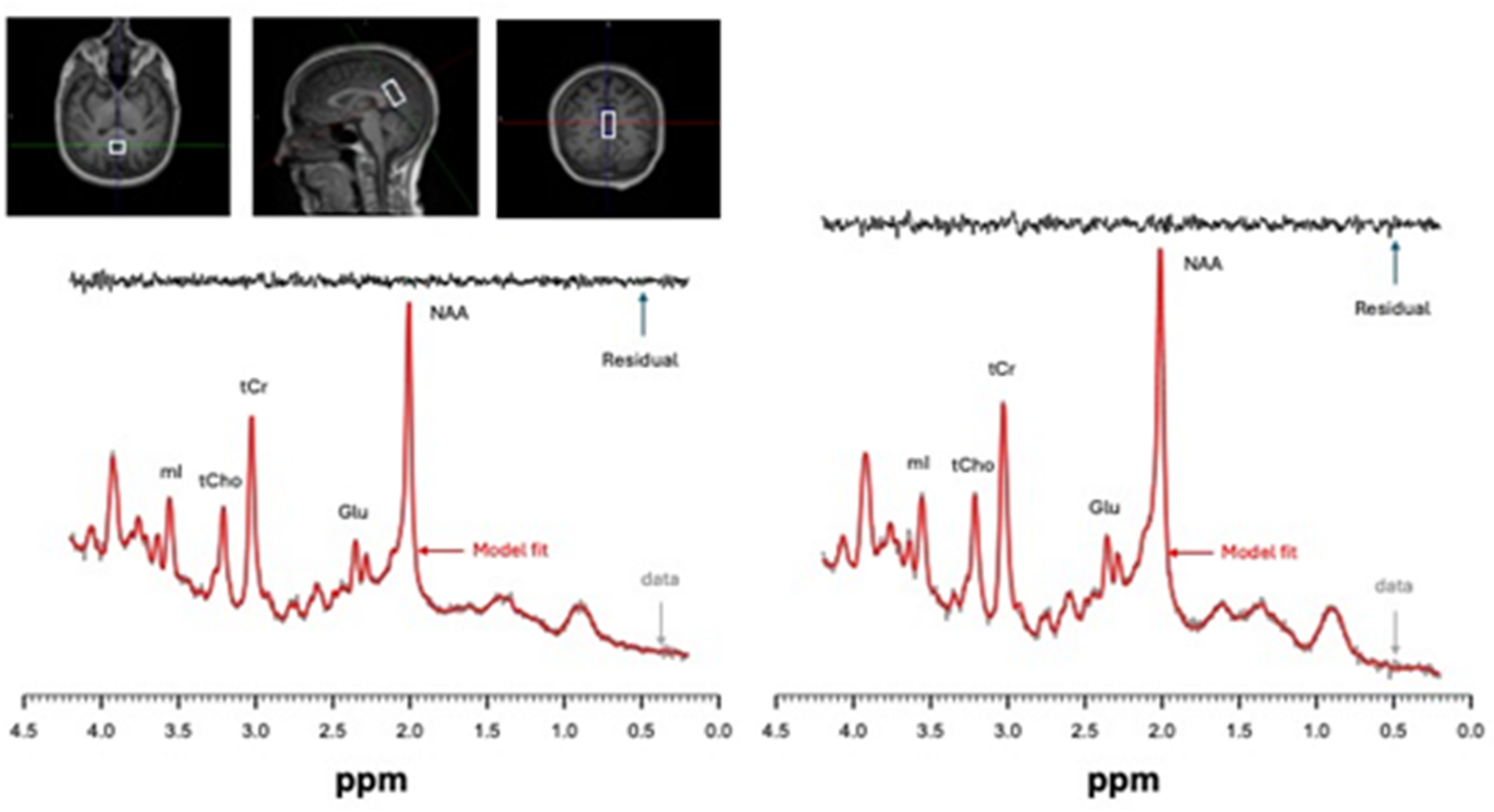
Abstract
In a longitudinal cohort study with intervention (NCT05216796), we utilized multiorgan imaging to determine if metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is associated with elevated cerebral glutamate and myo-inositol and to determine their sensitivity to dietary intervention. Fifty-five adults with self-reported MASLD or high MASLD risk (3 + metabolic risk factors) received liver and brain magnetic resonance spectroscopy scans pre and post two-week low carbohydrate (≤30 g/d) or low-calorie (women ~ 1200 kcal/d; men ~ 1500 kcal/d) diet, both known for their ability to reduce liver fat. Forty-four adults completed the study (36 female, average age 54 years). Thirty out of 44 met clinical criterion for MASLD based on neuroimaging (≥ 5% hepatic triglycerides). Intervention was associated with significant decreases in liver fat fraction (mean difference = 3.101, 95% CI 2.104–4.099, p < 0.0001), glutamate (mean difference = 0.753, 95% CI 0.274–1.233, p = 0.0032) and myo-inositol (mean difference = 0.478, 95% CI 0.180–0.775, p = 0.0027) in patients with confirmed MASLD. Thus, MASLD may be a source of glutamate neurotoxicity and neuroinflammation and diet is an effective strategy for supporting brain as well as liver health.