2025-12-23 京都大学 iPS細胞研究所
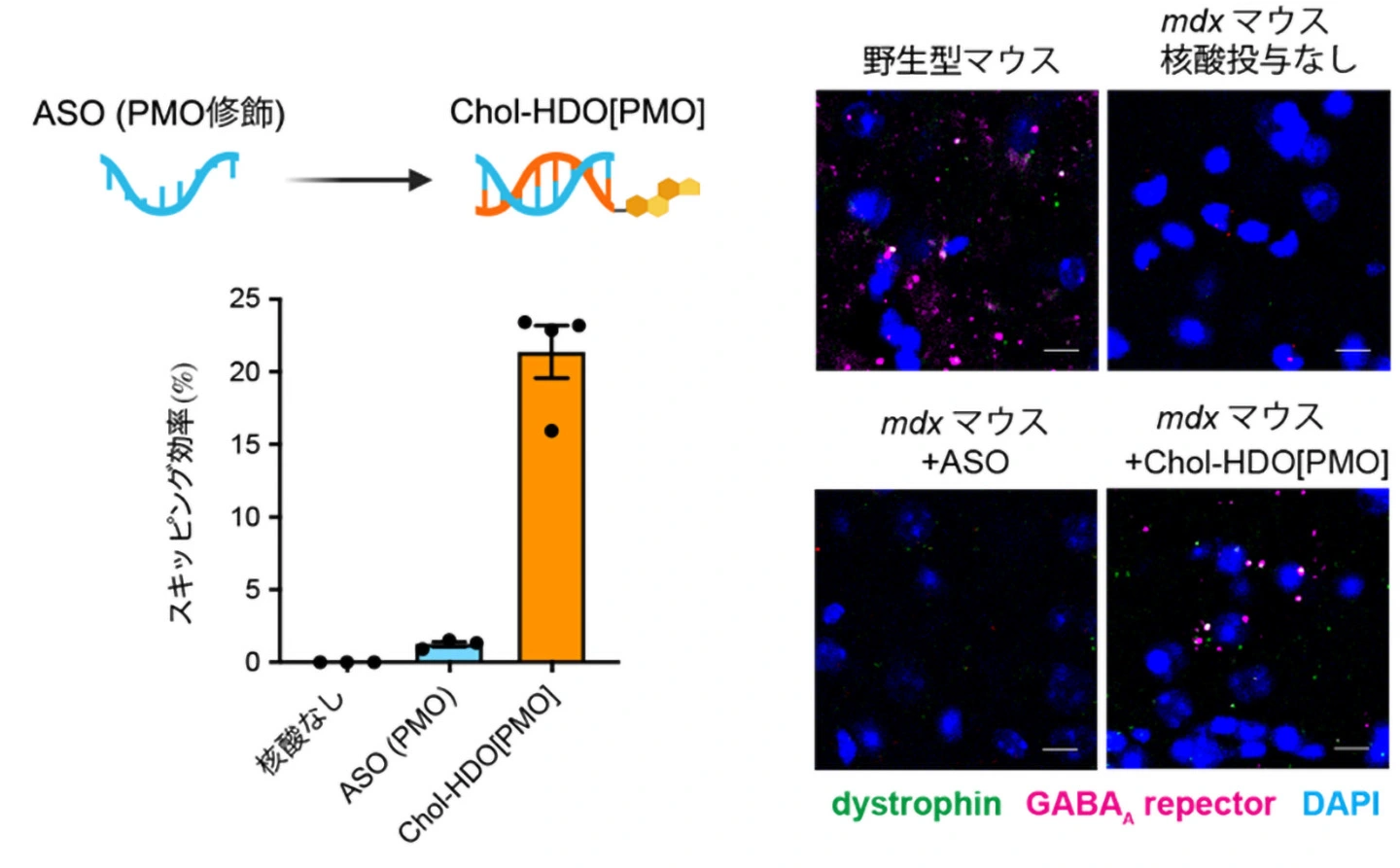
 Fig. 1 LNP-CRISPR投与後のエクソンスキッピング効率の比較
Fig. 1 LNP-CRISPR投与後のエクソンスキッピング効率の比較
<関連情報>
- https://www.cira.kyoto-u.ac.jp/j/pressrelease/news/251223-130000.html
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211124725014676
筋肉損傷に抵抗するためのLNP-CRISPR-Cas9による筋肉衛星細胞の編集 Muscle satellite cell editing by LNP-CRISPR-Cas9 to resist muscle injury
Taisuke Mochida, Naoko Fujimoto, Makoto Asahina, Shinya Asano, Shinsuke Araki, Naoto Inukai, Akitsu Hotta
Cell Reports Available online: 16 December 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116695
Highlights
- LNP-CRISPR edits muscle satellite cells more efficiently than AAV9-CRISPR
- ApoE is involved in the entry of LNP-CRISPR into satellite cells
- Exon skipping by LNP-CRISPR is tolerated upon muscle injury
- Restoration of satellite cells provides durable treatment for muscular dystrophy
Summary
Muscle satellite cells are essential for skeletal muscle regeneration and represent an attractive therapeutic target for gene delivery in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). However, efficient in vivo transduction of these cells has remained challenging. Here, we demonstrate that lipid nanoparticle (LNP)-mediated delivery of Streptococcus pyogenes CRISPR-Cas9 mRNA and guide RNA (LNP-CRISPR) induces exon skipping in Pax7-positive satellite cells more efficiently than adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors following intramuscular or intravenous administration in a DMD mouse model. Furthermore, unlike AAV-CRISPR, LNP-CRISPR-mediated genome editing showed greater resistance to repeated muscle injuries, indicating successful editing of regenerative satellite cells. These results highlight the potential of LNPs as a non-viral platform for durable genome editing in skeletal muscle and lay the foundation for developing safe and sustainable genome-editing therapies for DMD.