2026-01-20 中国科学院(CAS)
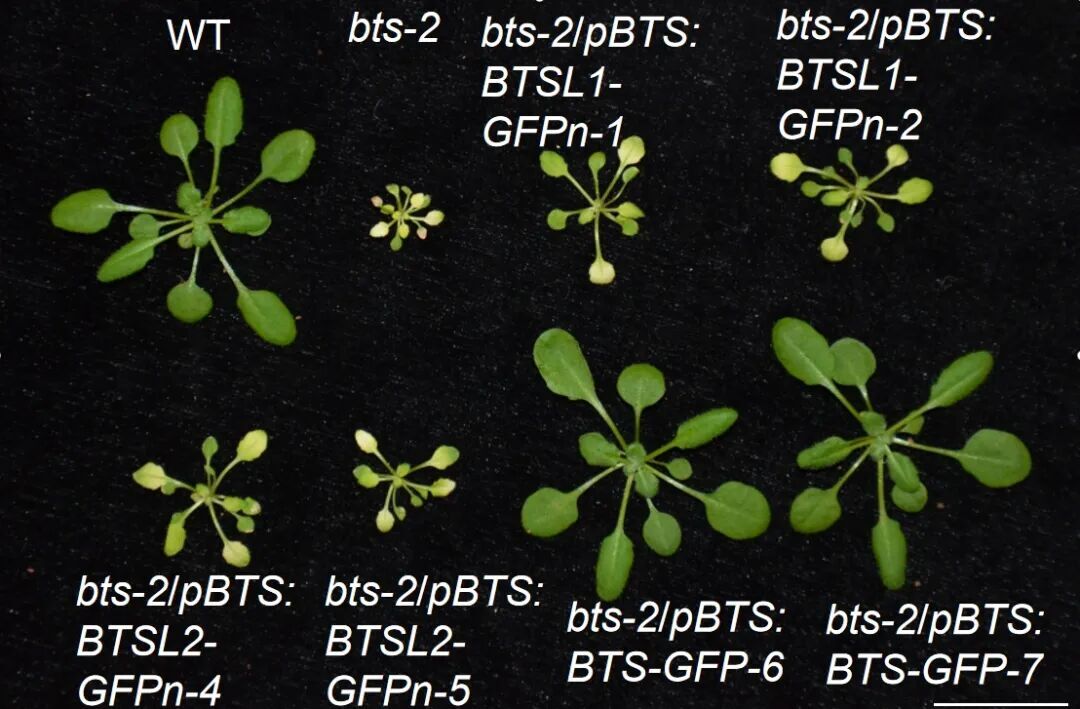

Growth of Arabidopsis thaliana under different treatments. (Image by ZHAO Junhui)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202601/t20260122_1146439.shtml
- https://academic.oup.com/plcell/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/plcell/koag006/8428452
アラビドプシスBRUTUS、BRUTUS-LIKE、bHLH IVcサブグループタンパク質は根と茎における鉄の恒常性を調整するArabidopsis BRUTUS, BRUTUS-LIKE, and bHLH IVc subgroup proteins coordinate iron homeostasis in the root and shoot
Junhui Zhao,Yang Li,Huaqian Ping,Rihua Lei,Bangzhen Pan,Gang Liang
The Plant Cell Published:16 January 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koag006
Abstract
Iron (Fe) deficiency threatens plant growth and health. In response to Fe deficiency, plants reprogram transcription in roots and shoots to maintain Fe homeostasis. However, the molecular mechanism by which Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) plants coordinate Fe deficiency responses in the root and shoot remains unclear. Here, we uncover the roles of BRUTUS (BTS), BTS-LIKE1 (BTSL1), and BTSL2, along with the bHLH IVc subgroup proteins (bHLH34, bHLH104, bHLH105, and bHLH115), in orchestrating the Fe deficiency responses of roots and shoots in Arabidopsis. BTS relieves shoot Fe toxicity and regulates Fe deficiency responses of shoots and roots, but BTSL1/2 are only involved in root Fe-deficiency responses. Furthermore, BTSL1/2 share similar molecular functions with BTS to a certain extent, as they also interact with bHLH IVc proteins and promote the degradation of bHLH105 and bHLH115. The simultaneous loss of the four bHLH IVc proteins completely halts the Fe deficiency responses across the whole plant. Moreover, bHLH IVc proteins are essential for BTSL1/2 functions in Fe deficiency responses. Meanwhile, bHLH IVc proteins directly enhance BTSL1/2 expression. This research sheds light on the distinct roles of BTS and BTSL1/2 in the root and shoot and emphasizes crucial roles of bHLH IVc proteins in regulating Fe deficiency responses in the root and shoot.