2022-08-03 フランクフルト大学
ドイツとアメリカの科学チームが、抗生物質生産菌の生合成を利用することに成功した。このプロセスでは、マクロライド系抗生物質の生体内合成の際に、小さな基質の一部としてフッ素原子を取り込みます。
これにより、天然物質中のフッ素の位置が非常に柔軟になり、その効果に影響を与えることができる。
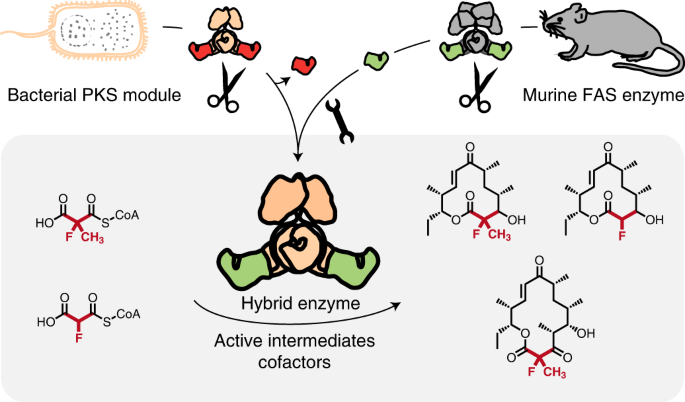
研究グループは、脂肪酸合成酵素と呼ばれる酵素のサブユニットを細菌のタンパク質に挿入することに成功した。この酵素は、マウスが本来持っている脂肪と脂肪酸の生合成に関与しているものである。脂肪酸合成酵素は、細菌の抗生物質製造にも重要な前駆体を処理する際に、あまり選択性がない。研究チームは、インテリジェントな製品設計により、マウスの酵素のサブユニットを、対応する抗生物質の生合成プロセスに組み込むことに成功した。
<関連情報>
- https://aktuelles.uni-frankfurt.de/englisch/a-new-biosynthesis-method-has-been-developed-to-produce-antibiotics-from-natural-substances/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-022-00996-z
化学酵素を用いたフッ素化ポリケチドの合成 Chemoenzymatic synthesis of fluorinated polyketides
Alexander Rittner,Mirko Joppe,Jennifer J. Schmidt,Lara Maria Mayer,Simon Reiners,Elia Heid,Dietmar Herzberg,David H. Sherman & Martin Grininger
Nature Chemistry Published:25 July 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-022-00996-z
Abstract
Modification of polyketides with fluorine offers a promising approach to develop new pharmaceuticals. While synthetic chemical methods for site-selective incorporation of fluorine in complex molecules have improved in recent years, approaches for the biosynthetic incorporation of fluorine in natural compounds are still rare. Here, we report a strategy to introduce fluorine into complex polyketides during biosynthesis. We exchanged the native acyltransferase domain of a polyketide synthase, which acts as the gatekeeper for the selection of extender units, with an evolutionarily related but substrate tolerant domain from metazoan type I fatty acid synthase. The resulting polyketide-synthase/fatty-acid-synthase hybrid can utilize fluoromalonyl coenzyme A and fluoromethylmalonyl coenzyme A for polyketide chain extension, introducing fluorine or fluoro-methyl units in polyketide scaffolds. We demonstrate the feasibility of our approach in the chemoenzymatic synthesis of fluorinated 12- and 14-membered macrolactones and fluorinated derivatives of the macrolide antibiotics YC-17 and methymycin.


