2023-10-04 リンショーピング大学
◆研究はオスロ大学病院とオスロ大学のKnut Dahl-Jørgensen氏によって主導され、ウイルスが糖尿病を引き起こす可能性を示す重要な一歩とされています。1型糖尿病は自己免疫疾患であり、治療法はなく、ウイルス感染との関連性が以前から指摘されていました。
◆研究結果は、抗ウイルス治療が1型糖尿病の進行を遅らせる可能性があることを示唆し、病気の発症前にこの治療法を検討する重要性を強調しています。
<関連情報>
- https://liu.se/en/news-item/antivirala-lakemedel-vid-typ-1-diabetes
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-023-02576-1
新規発症1型糖尿病におけるプレコナリルおよびリバビリン:第2相ランダム化試験 Pleconaril and ribavirin in new-onset type 1 diabetes: a phase 2 randomized trial
Lars Krogvold,Ida Maria Mynarek,Erica Ponzi,Freja Barrett Mørk,Trine Witzner Hessel,Trine Roald,Nina Lindblom,Jacob Westman,Peter Barker,Heikki Hyöty,Johnny Ludvigsson,Kristian F. Hanssen,Jesper Johannesen & Knut Dahl-Jørgensen
Nature Medicine Published:04 October 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-023-02576-1
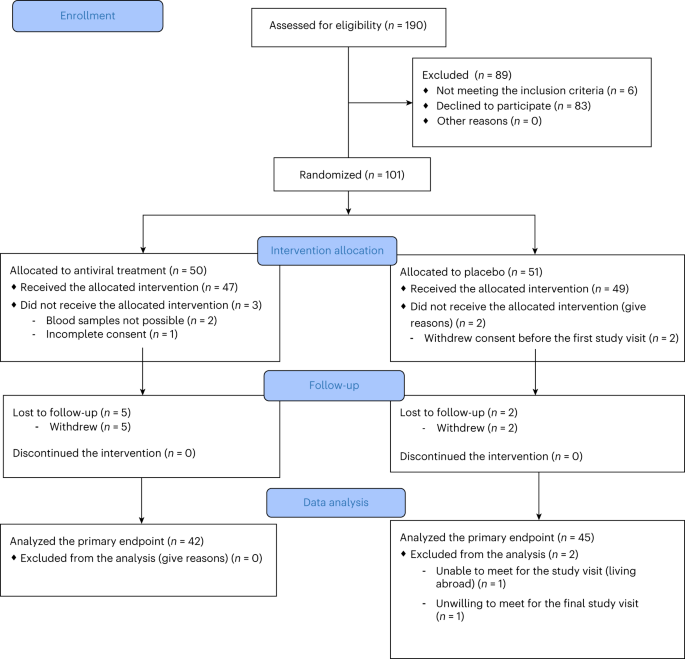
Abstract
Previous studies showed a low-grade enterovirus infection in the pancreatic islets of patients with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes (T1D). In the Diabetes Virus Detection (DiViD) Intervention, a phase 2, placebo-controlled, randomized, parallel group, double-blind trial, 96 children and adolescents (aged 6–15 years) with new-onset T1D received antiviral treatment with pleconaril and ribavirin (n = 47) or placebo (n = 49) for 6 months, with the aim of preserving β cell function. The primary endpoint was the mean stimulated C-peptide area under the curve (AUC) 12 months after the initiation of treatment (less than 3 weeks after diagnosis) using a mixed linear model. The model used longitudinal log-transformed serum C-peptide AUCs at baseline, at 3 months, 6 months and 1 year. The primary endpoint was met with the serum C-peptide AUC being higher in the pleconaril and ribavirin treatment group compared to the placebo group at 12 months (average marginal effect = 0.057 in the linear mixed model; 95% confidence interval = 0.004–0.11, P = 0.037). The treatment was well tolerated. The results show that antiviral treatment may preserve residual insulin production in children and adolescent with new-onset T1D. This provides a rationale for further evaluating antiviral strategies in the prevention and treatment of T1D. European Union Drug Regulating Authorities Clinical Trials identifier: 2015-003350-41.