新たな研究により、COVID-19から完全に回復した患者さんと長いコビッドを発症した患者さんの血液中に、分子シグネチャーの違いがあることがわかりました。 New research has found molecular signature differences in the blood of patients who fully recover from Covid-19 and those who develop long Covid.
2023-04-05 カーディフ大学
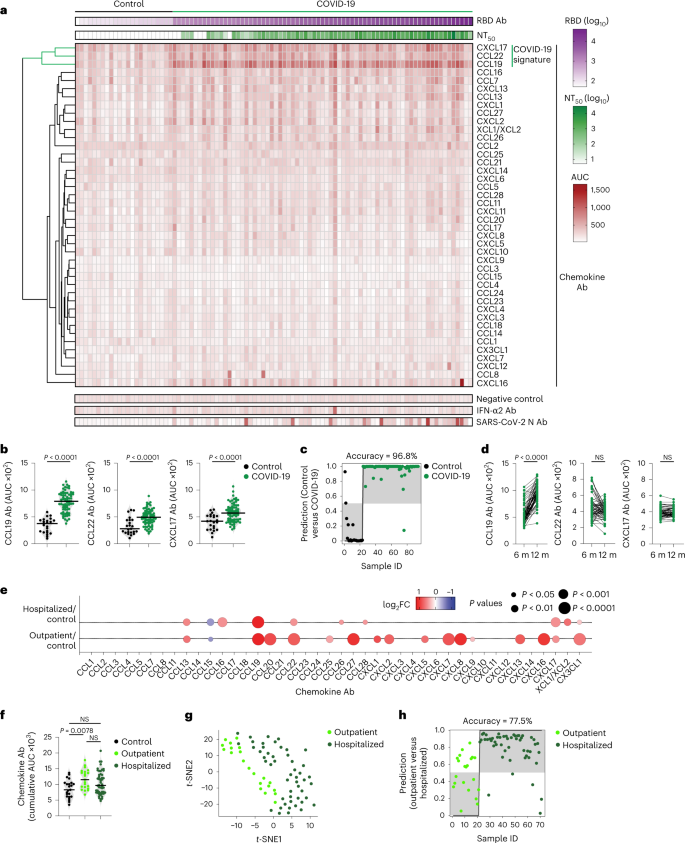
この研究は、ウェールズのカーディフ大学が行い、COVID-19患者の血液サンプルを調べ、回復した人々と長期合併症を発症した人々の免疫反応の違いを明らかにした。長期合併症を発症した患者は、炎症性免疫応答を調整するために分泌されるタンパク質であるケモカインの異なるレベルを示し、このタンパク質に対する自己抗体が欠落していることが分かった。これにより、長期的な炎症が引き起こされることが示唆され、回復した患者では、自己抗体が炎症を抑え、病気を解決する一方、長期合併症を発症した患者では、この自己抗体が欠落していることが分かった。
今回の研究は、長期的な炎症を引き起こす長期合併症を予防するための新しい治療法を開発する可能性を示唆している。
<関連情報>
- https://www.cardiff.ac.uk/news/view/2713678-blood-differences-in-long-covid-patients
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41590-023-01445-w
SARS-CoV-2感染後のケモカインに対する自己抗体と疾患経過の相関性 Autoantibodies against chemokines post-SARS-CoV-2 infection correlate with disease course
Jonathan Muri,Valentina Cecchinato,Andrea Cavalli,Akanksha A. Shanbhag,Milos Matkovic,Maira Biggiogero,Pier Andrea Maida,Jacques Moritz,Chiara Toscano,Elaheh Ghovehoud,Raffaello Furlan,Franca Barbic,Antonio Voza,Guendalina De Nadai,Carlo Cervia,Yves Zurbuchen,Patrick Taeschler,Lilly A. Murray,Gabriela Danelon-Sargenti,Simone Moro,Tao Gong,Pietro Piffaretti,Filippo Bianchini,Virginia Crivelli,Lucie Podešvová,Mattia Pedotti,David Jarrossay,Jacopo Sgrignani,Sylvia Thelen,Mario Uhr,Enos Bernasconi,Andri Rauch,Antonio Manzo,Adrian Ciurea,Marco B. L. Rocchi,Luca Varani,Bernhard Moser,Barbara Bottazzi,Marcus Thelen,Brian A. Fallon,Onur Boyman,Alberto Mantovani,Christian Garzoni,Alessandra Franzetti-Pellanda,Mariagrazia Uguccioni & Davide F. Robbiani
Nature Immunology Published:06 March 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-023-01445-w
Abstract
Infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 associates with diverse symptoms, which can persist for months. While antiviral antibodies are protective, those targeting interferons and other immune factors are associated with adverse coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outcomes. Here we discovered that antibodies against specific chemokines were omnipresent post-COVID-19, were associated with favorable disease outcome and negatively correlated with the development of long COVID at 1 yr post-infection. Chemokine antibodies were also present in HIV-1 infection and autoimmune disorders, but they targeted different chemokines compared with COVID-19. Monoclonal antibodies derived from COVID-19 convalescents that bound to the chemokine N-loop impaired cell migration. Given the role of chemokines in orchestrating immune cell trafficking, naturally arising chemokine antibodies may modulate the inflammatory response and thus bear therapeutic potential.