2024-02-14 カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校(UCSD)
<関連情報>
- https://today.ucsd.edu/story/researchers-uncover-mechanisms-behind-enigmatic-shapes-of-nuclei
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07086-9
核の形態はループ押し出しプログラムによって形成される Nuclear morphology is shaped by loop-extrusion programs
Indumathi Patta,Maryam Zand,Lindsay Lee,Shreya Mishra,Alexandra Bortnick,Hanbin Lu,Arpita Prusty,Sara McArdle,Zbigniew Mikulski,Huan-You Wang,Christine S. Cheng,Kathleen M. Fisch,Ming Hu & Cornelis Murre
Nature Published:14 February 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07086-9
Abstract
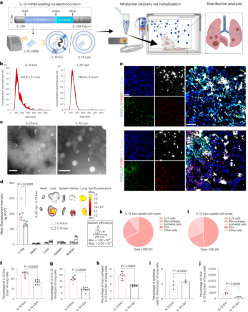
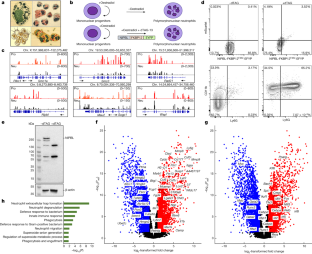
It is well established that neutrophils adopt malleable polymorphonuclear shapes to migrate through narrow interstitial tissue spaces1,2,3. However, how polymorphonuclear structures are assembled remains unknown4. Here we show that in neutrophil progenitors, halting loop extrusion—a motor-powered process that generates DNA loops by pulling in chromatin5—leads to the assembly of polymorphonuclear genomes. Specifically, we found that in mononuclear neutrophil progenitors, acute depletion of the loop-extrusion loading factor nipped-B-like protein (NIPBL) induced the assembly of horseshoe, banded, ringed and hypersegmented nuclear structures and led to a reduction in nuclear volume, mirroring what is observed during the differentiation of neutrophils. Depletion of NIPBL also induced cell-cycle arrest, activated a neutrophil-specific gene program and conditioned a loss of interactions across topologically associating domains to generate a chromatin architecture that resembled that of differentiated neutrophils. Removing NIPBL resulted in enrichment for mega-loops and interchromosomal hubs that contain genes associated with neutrophil-specific enhancer repertoires and an inflammatory gene program. On the basis of these observations, we propose that in neutrophil progenitors, loop-extrusion programs produce lineage-specific chromatin architectures that permit the packing of chromosomes into geometrically confined lobular structures. Our data also provide a blueprint for the assembly of polymorphonuclear structures, and point to the possibility of engineering de novo nuclear shapes to facilitate the migration of effector cells in densely populated tumorigenic environments.