大脳扁桃体回路の5-7Hzの振動と共感反応の因果関係を初めて解明 First identification of the causal relationship between 5-7 Hz oscillations in the cingulo-amygdala circuit and empathic response
2022-12-02 韓国基礎科学研究院(IBS)
研究チームは、この観察恐怖モデルと光遺伝学実験を組み合わせ、共感の起源を探った。注目すべきは、共感を引き起こすには、複数の脳領域内の脳リズムの同期が不可欠であることを明らかにしたことである。特に、前帯状皮質(ACC)と外側扁桃体(BLA)の間の同期が、直接体験による恐怖ではなく、他者の苦痛に間接的に触れることによる共感的恐怖に特有であることを明らかにした。
<関連情報>
- https://www.ibs.re.kr/cop/bbs/BBSMSTR_000000000738/selectBoardArticle.do?nttId=22266&pageIndex=1&searchCnd=&searchWrd=
- https://www.cell.com/neuron/fulltext/S0896-6273(22)01000-5
マウスにおける感情移入を促進する帯状扁桃体回路の半球側面化したリズム振動 Hemispherically lateralized rhythmic oscillations in the cingulate-amygdala circuit drive affective empathy in mice
Seong-Wook Kim,Minsoo Kim,Jinhee Baek,Charles-Francois Latchoumane,Gireesh Gangadharan,Yongwoo Yoon,Duk-Soo Kim,Jin Hyung Lee,Hee-Sup Shin
Neuron Published:December 01, 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2022.11.001
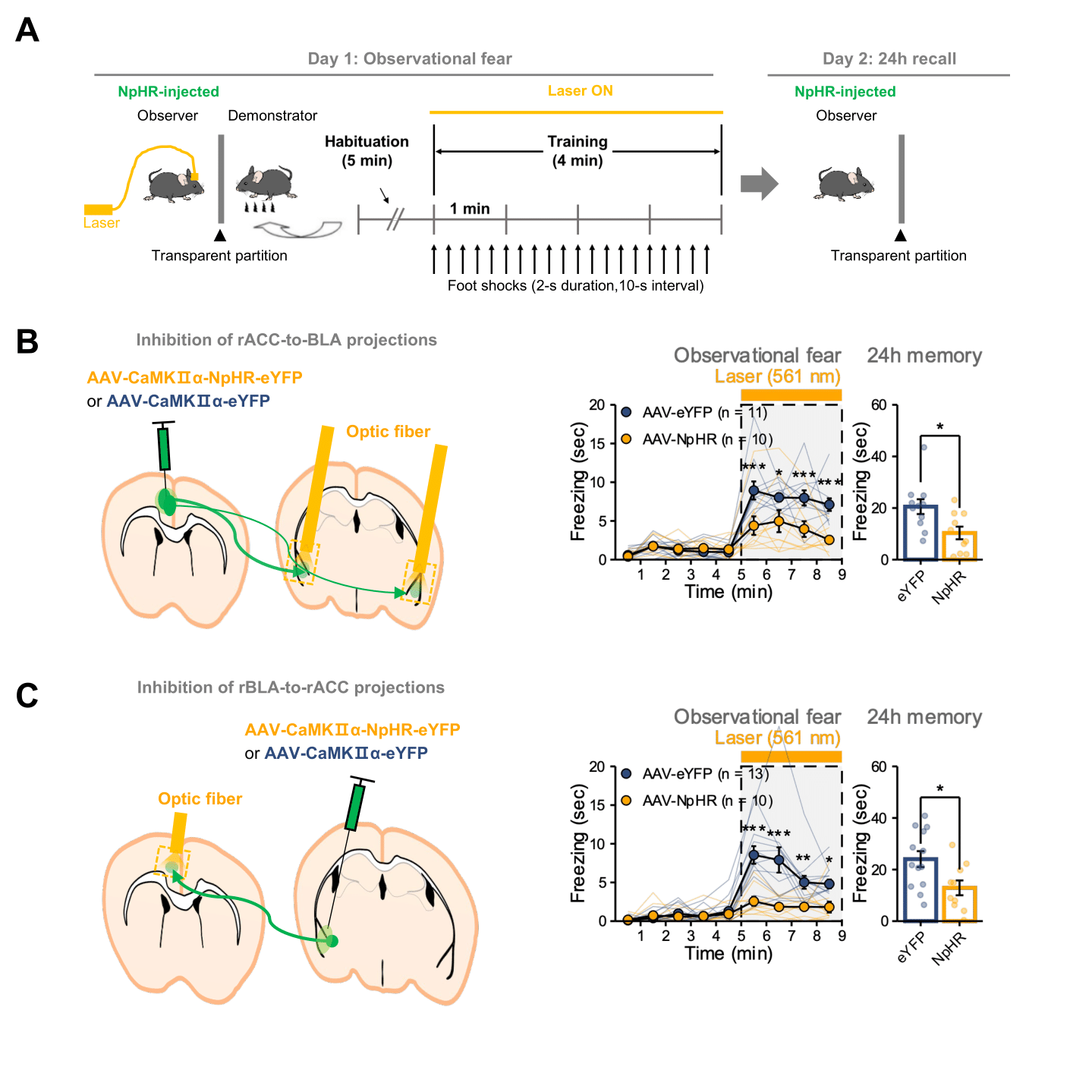
Highlights
•The lateralized rACC-rBLA circuit is responsible for observational fear (OF)
•5–7 Hz oscillations in rACC and rBLA increase during OF
•5–7 Hz oscillations in rACC and rBLA are causally involved in OF
•Hippocampal type-2 theta bi-directionally modulates the ACC-BLA theta and OF
Summary
Observational fear, a form of emotional contagion, is thought to be a basic form of affective empathy. However, the neural process engaged at the specific moment when socially acquired information provokes an emotional response remains elusive. Here, we show that reciprocal projections between the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and basolateral amygdala (BLA) in the right hemisphere are essential for observational fear, and 5–7 Hz neural oscillations were selectively increased in those areas at the onset of observational freezing. A closed-loop disruption demonstrated the causal relationship between 5–7 Hz oscillations in the cingulo-amygdala circuit and observational fear responses. The increase/decrease in theta power induced by optogenetic manipulation of the hippocampal theta rhythm bi-directionally modulated observational fear. Together, these results indicate that hippocampus-dependent 5–7 Hz oscillations in the cingulo-amygdala circuit in the right hemisphere are the essential component of the cognitive process that drives empathic fear, but not freezing, in general.


