2023-07-10 ライス大学
◆この技術は、心臓病や消化器疾患などの治療法の改善につながる可能性があります。光刺激によって回転する小分子アクチュエータを使用し、滑筋細胞にカルシウムシグナル応答を誘発させました。特に心筋において細胞間のシグナル伝播を制御することが可能であり、不整脈の緩和など、心臓機能に対する精密な分子レベルの制御が可能になるかもしれません。
<関連情報>
- https://news.rice.edu/news/2023/light-activated-molecular-machines-get-cells-talking
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-023-01436-w
分子機械が細胞間カルシウム波を刺激し筋収縮を引き起こす Molecular machines stimulate intercellular calcium waves and cause muscle contraction
Jacob L. Beckham,Alexis R. van Venrooy,Soonyoung Kim,Gang Li,Bowen Li,Guillaume Duret,Dallin Arnold,Xuan Zhao,John T. Li,Ana L. Santos,Gautam Chaudhry,Dongdong Liu,Jacob T. Robinson & James M. Tour
Nature Nanotechnology Published:10 July 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-023-01436-w
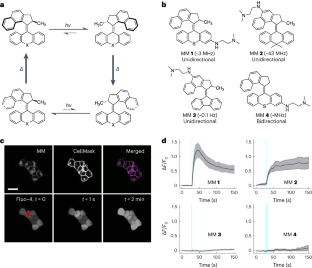
Abstract
Intercellular calcium waves (ICW) are complex signalling phenomena that control many essential biological activities, including smooth muscle contraction, vesicle secretion, gene expression and changes in neuronal excitability. Accordingly, the remote stimulation of ICW could result in versatile biomodulation and therapeutic strategies. Here we demonstrate that light-activated molecular machines (MM)—molecules that perform mechanical work on the molecular scale—can remotely stimulate ICW. MM consist of a polycyclic rotor and stator that rotate around a central alkene when activated with visible light. Live-cell calcium-tracking and pharmacological experiments reveal that MM-induced ICW are driven by the activation of inositol-triphosphate-mediated signalling pathways by unidirectional, fast-rotating MM. Our data suggest that MM-induced ICW can control muscle contraction in vitro in cardiomyocytes and animal behaviour in vivo in Hydra vulgaris. This work demonstrates a strategy for directly controlling cell signalling and downstream biological function using molecular-scale devices.